EXTRACTION
Extraction is used to attain potentially therapeutic portions from medicinal plants and to eliminate undesired portions/material.
Phytochemicals (phyto=plant) are chemicals naturally produced by plants to help the plants growth or defense against competitors, pathogens, or predator. Phytochemicals are what make our food a medicine and make plants - apart from phytotoxins- , medicine.
Medicinal Plants % of Use - International Journal of Herbal Medicine
Fractional Extraction of Phytochemicals can be done using a vast number of solvents and techniques for separating a fraction from other(s). It relies on the variable solubility of different compounds in different substances (solvents; Solvents properties (physical and chemical) is the start point when choosing a solvent for a particular purpose.) and the variable physical properties.
Major phytochemicals in food by color
Techniques used for medicinal phytochemicals extraction are vast and include expression, maceration, infusion, percolation, digestion, decoction, hot continuous extraction (Soxhlet), aqueous-alcoholic extraction by fermentation, phytonic extraction (with hydrofluorocarbon solvents).
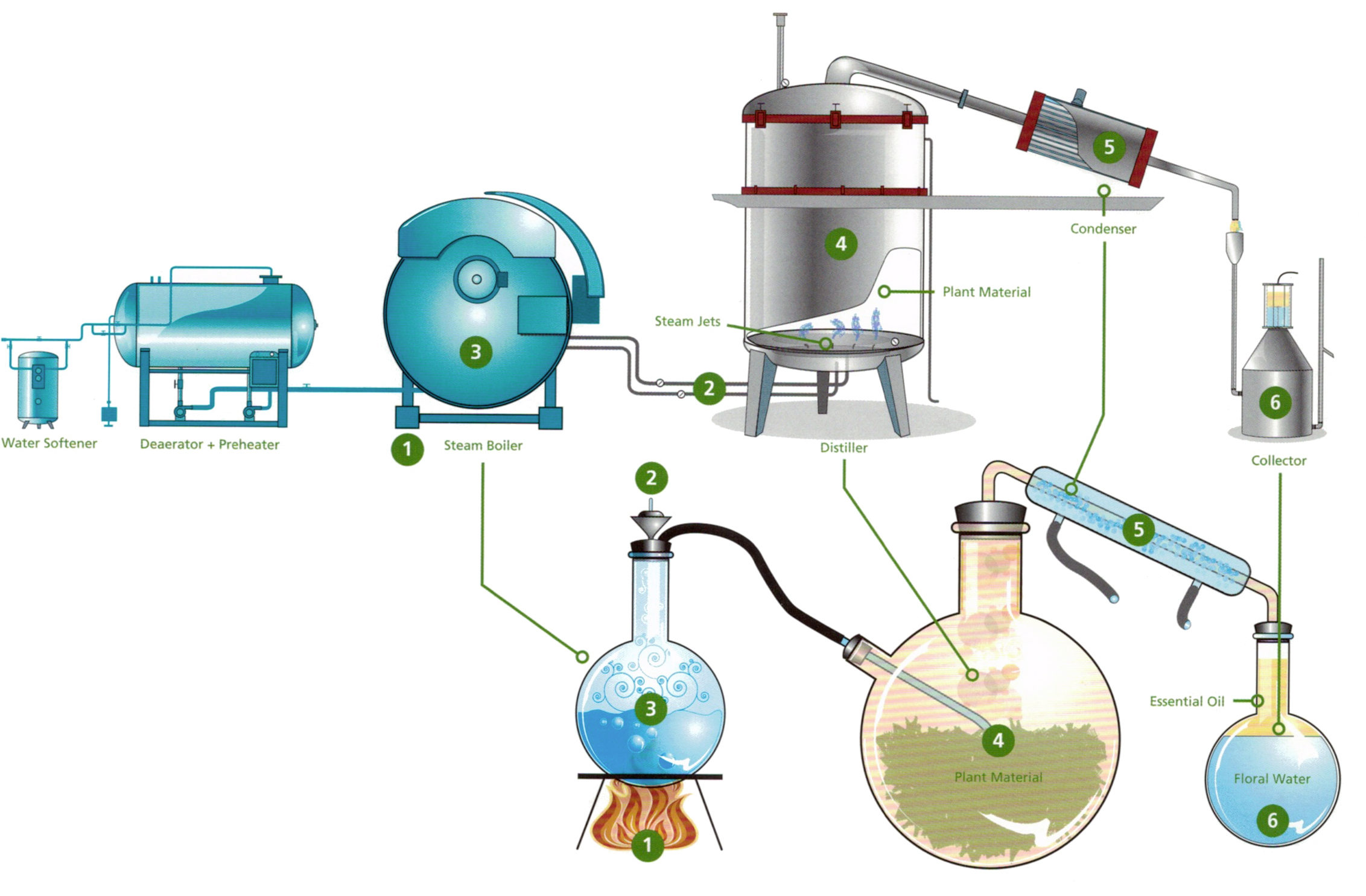
For aromatic plants, hydrodistillation techniques (water distillation, steam distillation, water and steam distillation), hydrolytic maceration followed by distillation, expression and enfleurage (cold fat extraction) are common.
Latest extraction methods for aromatic plants include headspace trapping, solid phase micro-extraction, protoplast extraction, micro-distillation, thermo-micro-distillation, and molecular distillation, countercurrent extraction, microwave-assisted extraction, ultrasound extraction (sonication), supercritical fluid extraction, and physical method for their dispersion (ultra-sound apparatus), has led for the first time to a good solubility, diffusion and dispersion of the essential oil in water, thus ensuring a better contact of these oils and/or their constituents with tested organisms.
Physical method for dispersion (ultra-sound apparatus), has a good solubility, diffusion and dispersion of the essential oil in water, thus ensuring a better contact of these oils and/or their constituents with tested cells.
Distillation
The process for absolute or preferential separation of component(s) from a mixture by heating evaporation then condensation.
Commonly used for liquid/semiliquid mixtures or solids (plant tissue/extract in solvent - commonly water). The behavior of mixture to be distilled is largely determined by its type as a miscible or immiscible mixture.
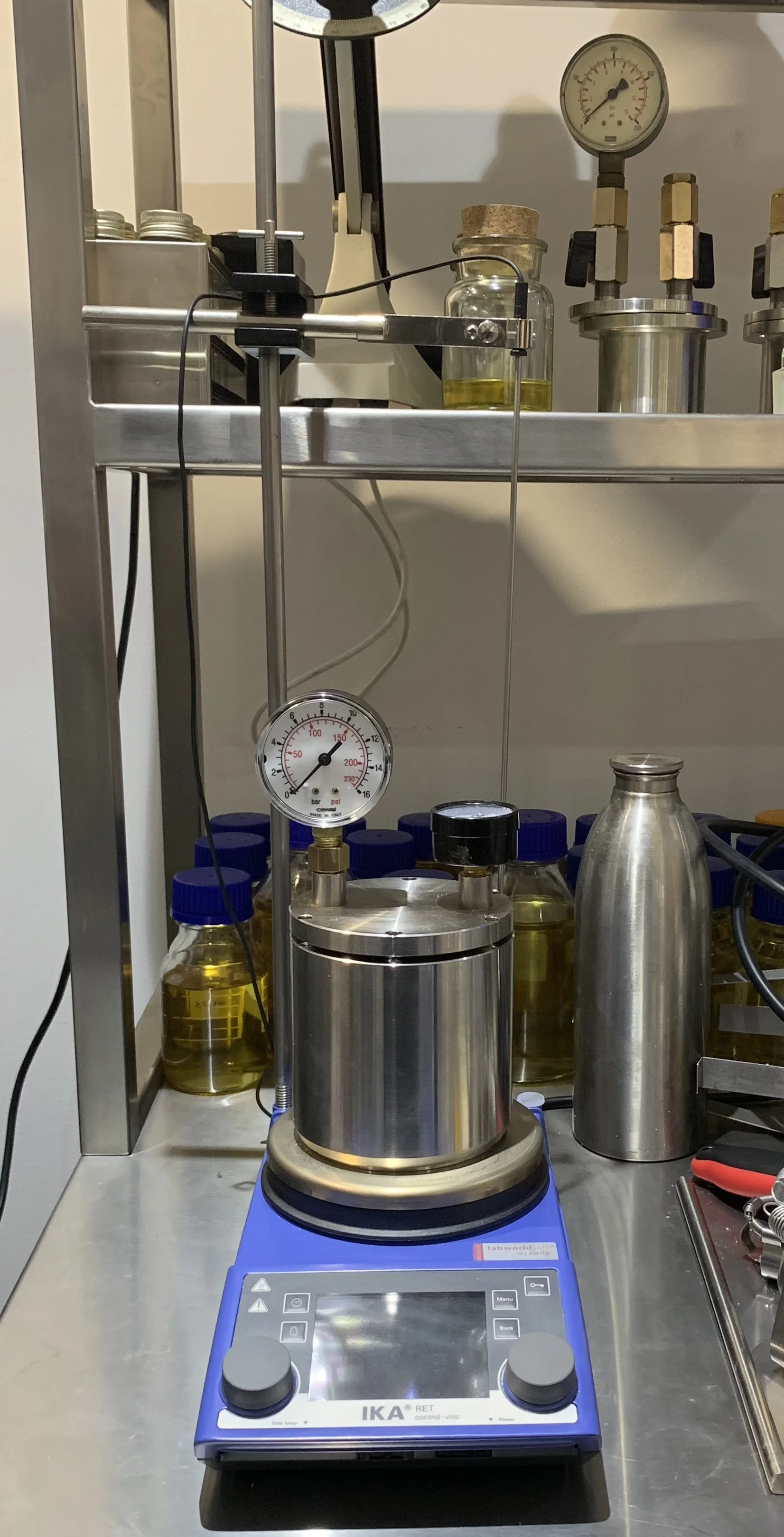
Water hydro-distilation
The most traditional and simple one. The material to be distilled is loaded with water into the still. Mainly used for non-cellular materials (like resin and gum).Enable control of operating pressure (and hence temperature) when vacuum is included.
Wet Steam distillation
Modified form of the earlier water hydrodistillation. Serve mainly for cellular materal distillation where steam "destroy" cellular walls of plant material and so enable a more efficient distillation.
Dry steam distillation
Advanced from wet steam distillation and serve mainly performance and efficiency. Use superheated steam and hence called dry.
Frankincense & Myrrh essential oils
Water Hydrodistillation is ideal for extracting all plant resin essential oils as it is;
1- Non-cellular matter.
2- Enable control over operating temperature and pressure, in addition to time.
3- Enable pre-distillation processing like frankincense mucilage preparation.
B. sacra essential oil yield by distillation is 4.5-5.3%. Essential oil yield rather than the duration of distillation should monitor distillation efficiency. Typically distillation is operated at 100C, atmospheric pressure with water: resin load ratio of 2.25:1 by weight.
Vacuum hydrodistiller used for B. sacra and C. myrrha distillation extraction.
Essential oils ideally should be kept in airtight stainless steel 316 grade containers away from direct sunlight and oxygen (that may require use of inert gas as a barrier) if meant to store for long time.
Treated aluminum containers can store it for 2 years.
Factors Influencing Essential Oils Stability:
1- Light
2- Temperature
3- Metal Contaminants
4- Oxygen Availability
Aluminum is lighter, cheaper and if properly lined (treated) would be suitable essential oil container for short terms. Stainless steel in the other hand can store essential oils for a life time if airtight and away from oxygen, and at temperatures lower than 6Cº.
Fractional Distillation
Fractional distillation is different from distillation in that it separates a miscible mixture into a number of different parts, called fractions, used to separate a mixture into its component parts, or fractions, such as in separating chemical compounds by their boiling point by heating them to a temperature at which one or more fractions of the compound will vaporize. Generally, the component parts boil at less than 25 °C from each other under a pressure of one atmosphere (1Bar). If the difference in boiling points is greater than 25 °C, a simple distillation is used.
The only difference in apparatus between simple and fractional distillation methods is the use of a fractionating column.
Short Bath fractional distillation
Ultrasonic assisted extraction
Ultrasound-assisted extraction has been used in diverse applications of food-processing technology to extract bioactive compounds from plant materials. Ultrasound, with levels greater than 20 kHz, is used to disrupt plant cell walls, which helps improve the solvent’s ability to penetrate the cells and cell disruption to obtain a higher extraction yield.
Ultrasound-assisted extraction can use a low operating temperature through processing, maintaining a high extract quality for compounds.
Ultrasound-assisted extraction uses high-frequency sound waves, Microwave-assisted extraction in the other hand uses non ionizing electromagnetic waves. Both techniques are considered green and safe but it's our research preferential to avoid it unless for parallel experiments (as a control).
Cold & Hot Press extraction
Extracting fixed oils from plant tissues can be either cold (low heat) or heated pressing.
Cold pressing oil has the advantage of usually higher quality. It can be more difficult to cold press some types of seeds and nuts. If more volume is required, turning to his heat press technique will increase the yield. But, heating process degrades the quality.
Hydraulic Cold Press
Supercritical fluid extraction
SFE is the process of separating one component (the extractant) from another (the matrix) using supercritical fluids as the extracting solvent. Extraction is usually from a solid matrix, but can also be from liquids. SFE can be used as a sample preparation step for analytical purposes, or on a larger scale to either strip unwanted material from a product (e.g. decaffeination) or collect the desired product (e.g. plant tissue oils). Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the most used supercritical fluid
CO2 SFE used for Boswellia sacra extraction.
Preparative flash chromatography
A chemical technology used to isolate a single chemical compound from a mixture. Chromatography is able to separate substances based on differential adsorption of compounds to the adsorbent; compounds move through the column at different rates, allowing them to be separated into fractions.
Pilot stage preparative flash chromatography.
Accelerated Solvent Extraction ASE™ & the Rocket™ evaporator from Dionex
Accelerated solvent extraction ASE™ is an extraction technique use high temperature and pressure with possible better recovery and has been used as a control.
The Rocket™ is to concentrate or dry large-volume samples rapidly and in parallel using an automated evaporator system.